Method for RNA structure comparison.
Sequence-agnostic method for RNA structure comparison in lncRNAs.
Long non-coding RNAs are essential regulators at all levels of cellular processes and interact with RNA-binding proteins and other molecules. Their misregulation leads to a wide spectrum of diseases, including cancer and immune disorders. While their sequences are usually poorly conserved, lncRNA secondary structures often are, underlining their functional relevance. Despite the continuous growth of RNA structural data, efficient tools to compare and identify conserved structures remain limited.
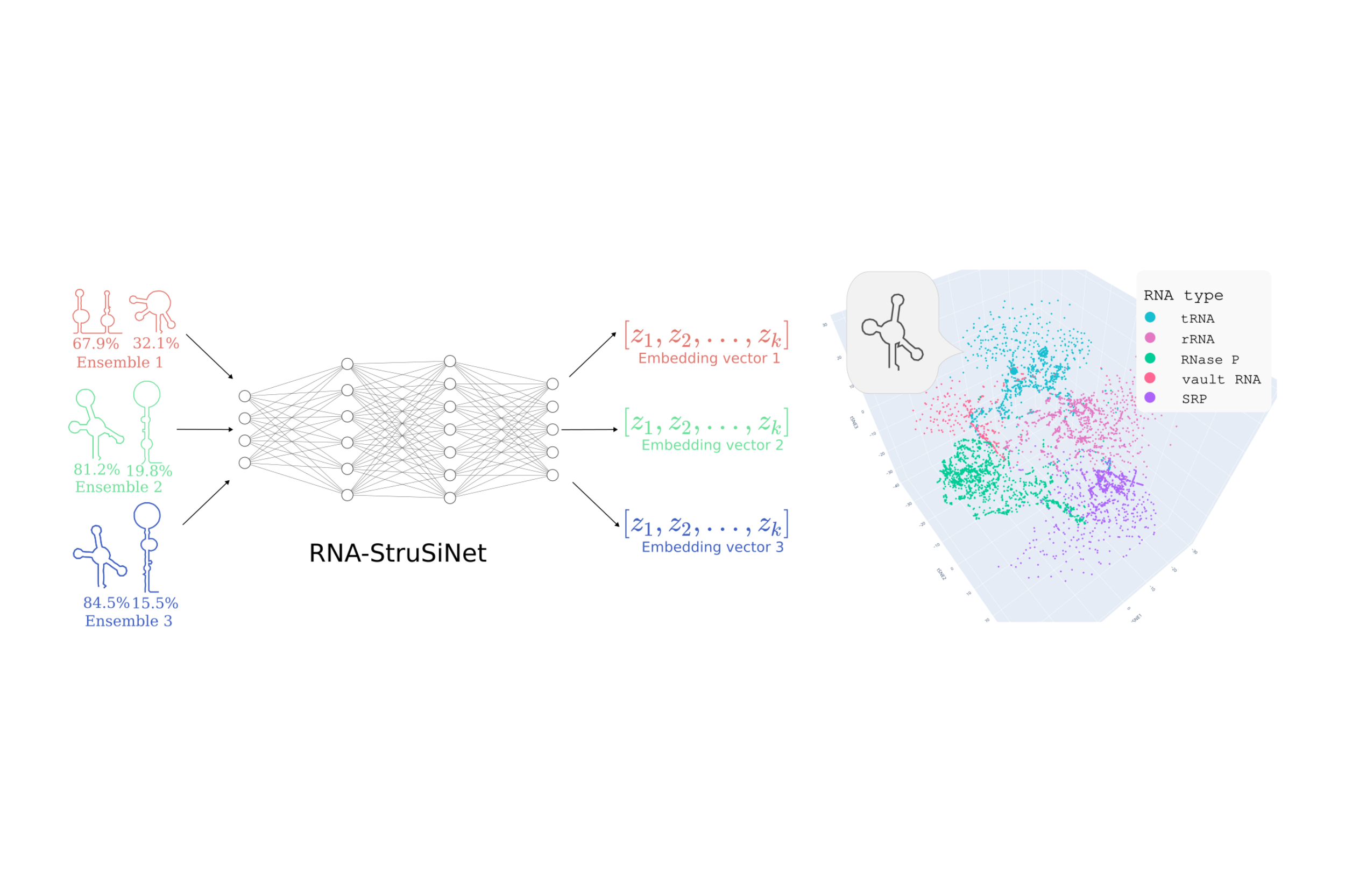
In this project, we suggest using the Siamese Convolutional Neural Network (SCNN) to analyze RNA secondary structure. SCNNs, proven in tasks such as face recognition, calculate structural similarities without the need for sequence alignment, thereby overcoming significant limitations of traditional methods. Preliminary results using RNases P data illustrate that SCNNs can successfully identify conserved structures within RNA families and distinguish them from unrelated sequences.
Our approach will explore conserved lncRNA structures by integrating datasets from experimental approaches like SHAPE. This project aims to explain how conserved motifs underpin lncRNA functions, further understanding their role in diseases, and uncover new therapeutic opportunities.